Overview The WebSocket Mechanism
This article introduces What’s the Websocket and how it works.
WebSocket is a popular tool in HTTP 1.1, that realized full-duplex on HTTP model. It upgrades HTTP 1.1 to let the TCP channel still open until the request or response side closes the communication channel.
In the past without the WebSocket age, there are two mechanisms to achieve duplex. One is "Long Polling" the other one is "HTTP stream", they manipulate the request channel time to simulate duplex[1]. On the other worlds, that just don't close HTTP Request. But it have a drawback that caused server big loading but WebSocket can solve these problem
Detail in attachment about " Long Polling" and " HTTP Stream"
The Design of Websockets
The WebSocket build connection have two steps. Client should start TCP connection and then use HTTP GET to verify HTTP upgrade process (Websocket HandShake) before staring transmit data.

WebSocket handshake
WebScoket handshake base on HTTP 1.1 to do this. The main purpose is client side tells HTTP Server we want to upgrade to WebSocket.(Figure WebSocket handshake sequence diagram)
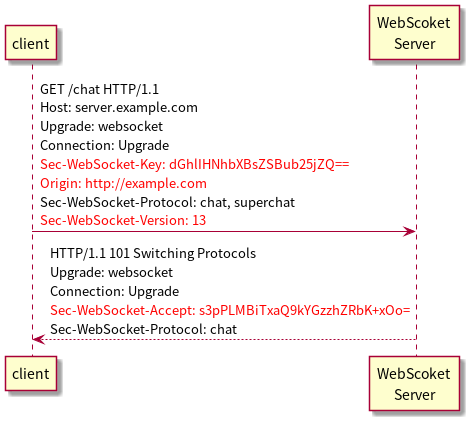
Something Important: ● Sec-WebSocket-key, Sec-Websocket-Accept: The purpose is that proves the handshake was received \1. Sec-Websocket-key is a UUID that encoded by Base64. \2. Sec-Websocket-Accept is the string that Sec-Websocket-key concatenates with decode of Sec-Websocket-key. The string will encode SHA-1 and encode Base64 before send back it.

● Origin: The Origin header field is used to protect against unauthorized cross-origin use of a WebSocket server by scripts using the WebSocket API in a web browser. example: if code downloaded from www.example.com attempts to establish a connection to ww2.example.com, the value of the header field would be "http://www.example.com"
● Sec-WebSocket-Version: The value of this header field MUST be 13.
Three Control Frame: Ping, Pong, Close
● Ping Upon receipt of a Ping frame, an endpoint MUST send a Pong frame in response, unless it already received a Close frame.
● Pong (not only reply ping but it can serve as a unidirectional heartbeat) If an endpoint receives not only one ping, that May elect the most recent ping to reply a Pong.

● Close If the endpoint receives a close control frame, it MUST send a Close frame in response.
Sometimes endpoint receive a close frame, but some data still transmit. In that situation, endpoint can send a close frame after this transmit.

Conclusion
WebSocket is so popular on Web event implementation but seldom do people realize how it works. In this article, have some essential knowledge to help people develop the WebSocket Application. Especially WebSocket handshake, so many modules should set these arguments.
Attachment: ● Long Polling: When a client sends a request but the server does not close this connection a period. if it is closed, the client will still resend a request to do it again.
● HTTP Stream: When the client sends a request but the server never closes this connection.
In both of them, the Server response still has an HTTP header and no mechanism to manage the endpoint connection status.
Reference [1]Loreto, S., et al. “RFC 6202-Known Issues and Best Practices for the Use of Long Polling and Streaming in Bidirectional HTTP.” IETF, Duben (2011). [2] Skvorc, Dejan, Matija Horvat, and Sinisa Srbljic. “Performance evaluation of Websocket protocol for implementation of full-duplex web streams.” 2014 37th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO). IEEE, 2014. [3]Fette, Ian, and Alexey Melnikov. “Rfc 6455: The websocket protocol.” IETF, December (2011).
Last updated